- It detects its prey with electroreceptive sensing organs.
- The sharp barb can be over 35 cm long and is filled with toxins.
- It typically inhabits large rivers with muddy or sandy bottom.
- can be over 35 cm long and is filled with toxins.
- The average disc width of offspring at birth is about 30 cm.
- They are not aggressive and do not readily attack humans.
- Historically, it was not considered a good food fish but often got caught as a bycatch.
- In some regions, there is increasing fishing pressure caused by the aquarium trade and sport fishing.
- It is assessed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List, with the Thailand subpopulation listed as Critically Endangered.
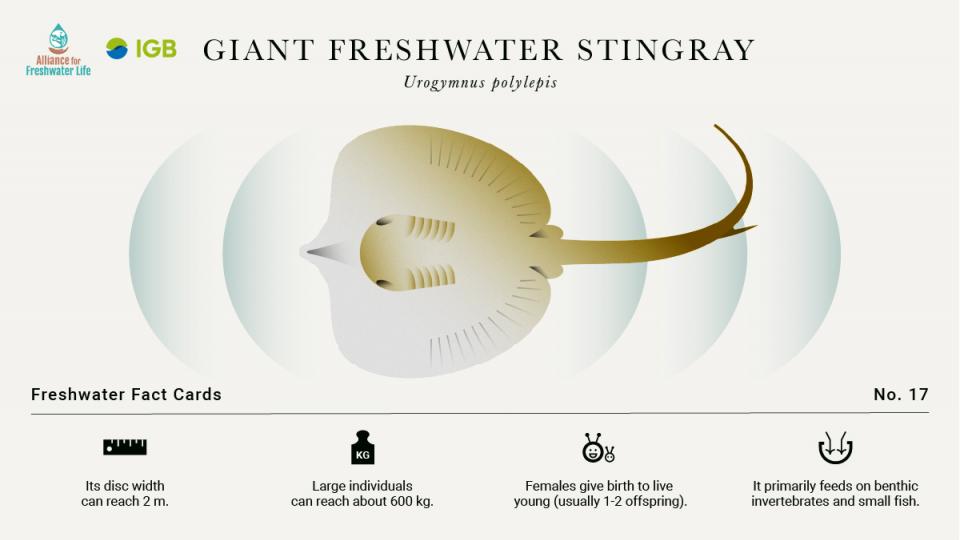
Its disc width can reach 2 m. Large individuals can reach about 600 kg. Females give birth to live young (usually 1-2 offspring). It primarily feeds on benthic invertebrates and small fish.
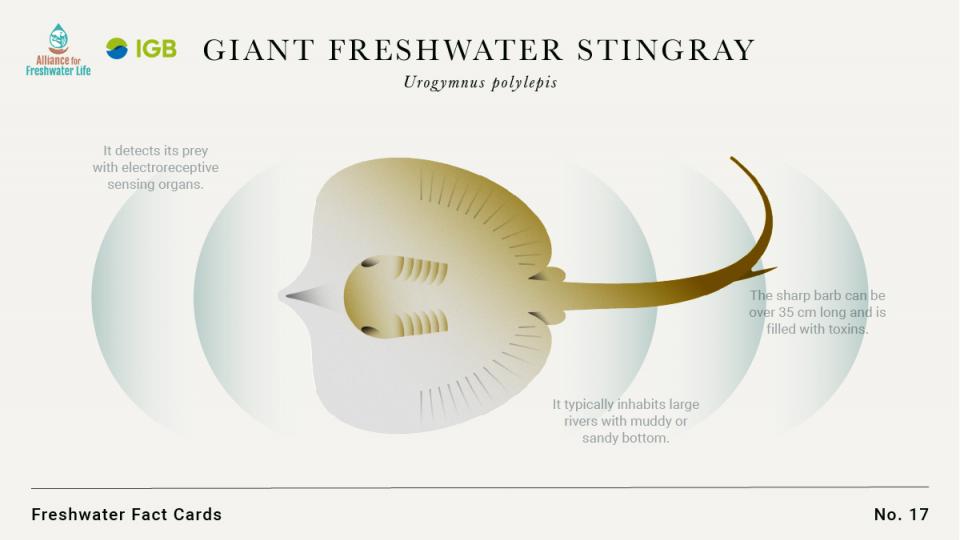
It detects its prey with electroreceptive sensing organs. It typically inhabits large rivers with muddy or sandy bottom. The sharp barb can be over 35 cm long and is filled with toxins.