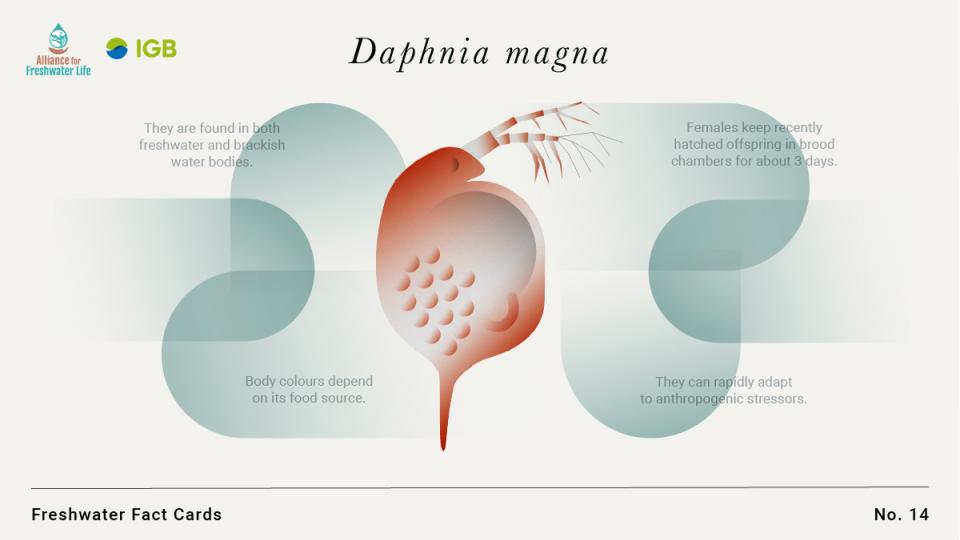
- They are found in both freshwater and brackish water bodies.
- They are susceptible to fish predation and often occur in fishless water bodies such as rocky pools and ponds.
- Body colours depend on its food source.
- Females can produce a clutch of eggs about every 2-4 days, with an average of 6-10 eggs (but can be over 100 eggs).
- Females keep recently hatched offspring in brood chambers for about 3 days.
- During large part of the growing season, females reproduce asexually with diploid eggs that all develop to females.
- In adverse environmental conditions, females produce haploid eggs that are fertilised by males.
- These dormant eggs can “rest” in the sediment for many years, until environmental conditions become favourable.
- They can rapidly adapt to anthropogenic stressors.
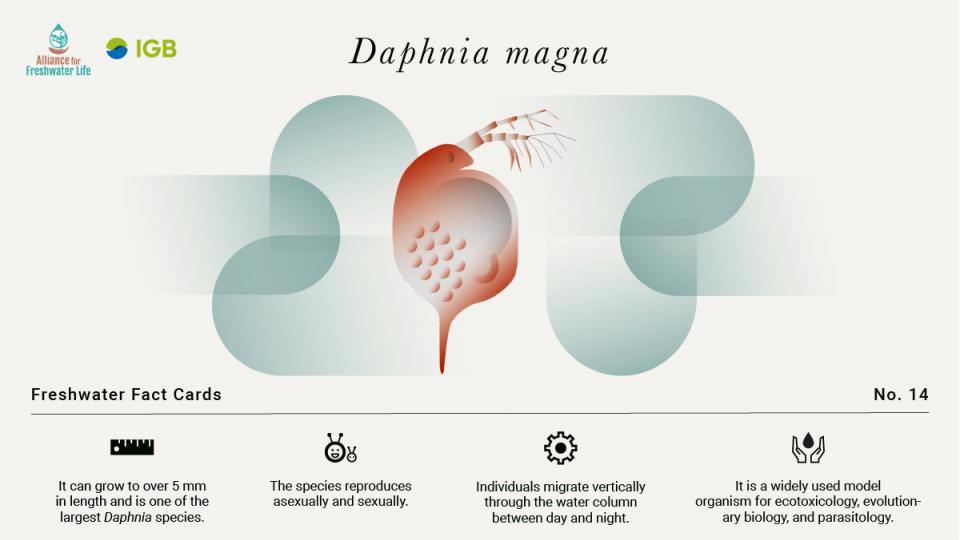
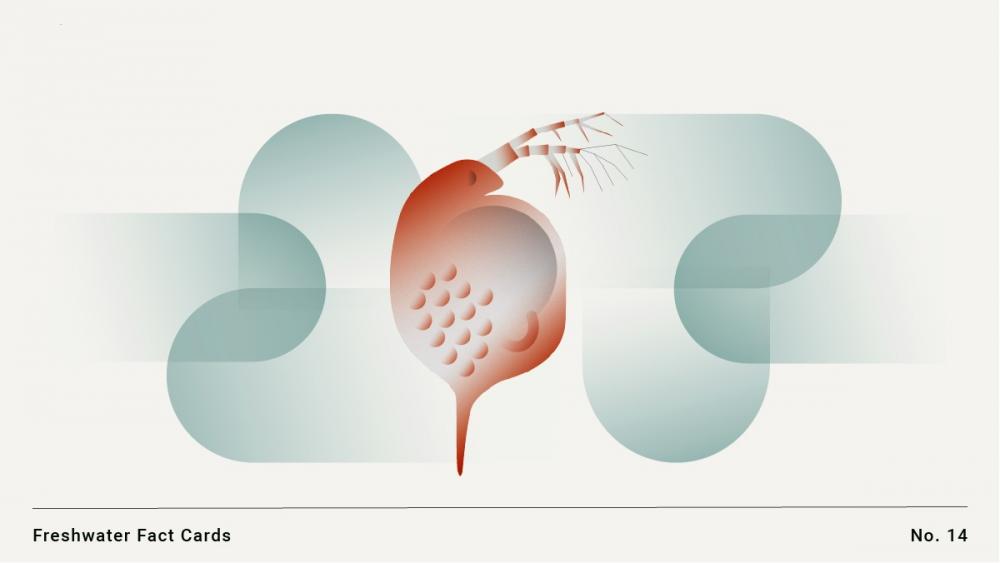
It can grow to over 5 mm in length and is one of the largest Daphnia species. The species reproduces asexually and sexually. Individuals migrate vertically through the water column between day and night. It is a widely used model organism for ecotoxicology, evolutionary biology, and parasitology.
They are found in both freshwater and brackish water bodies. Females keep recently hatched offspring in brood chambers for about 3 days. Body colours depend on its food source. They can rapidly adapt to anthropogenic stressors.







